Introduction: In the ever-expanding digital ecosystem, the unsung hero orchestrating the symphony of hardware and software programs inside personal computer systems is the Operating System (OS). From the moment you strengthen your PC to launching applications and handling files, the OS is the invisible conductor ensuring continuing and efficient user enjoyment. This article delves into the significance and functionalities of PC operating systems, exploring the numerous landscape that powers the devices vital to our daily lives.
Defining the PC Operating System:
An Operating System is the fundamental software that manages hardware assets and gives offerings for computer packages. In the context of personal computers, popular OS options consist of Microsoft Windows, macOS, and diverse Linux distributions.
Booting and Initialization:
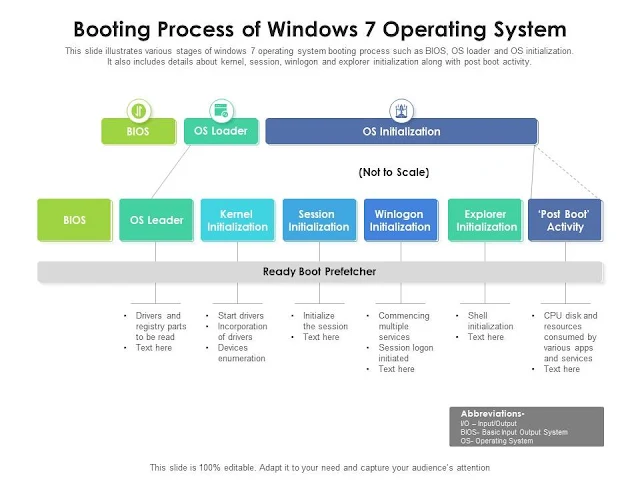
- The OS kicks into action the instant you power on your PC. This manner, referred to as booting, involves initializing hardware components, loading vital device files, and getting ready the device for consumer interplay.
- Boot loaders, together with GRUB or the Windows Boot Manager, facilitate the loading of the OS kernel.
User Interface (UI):
- The User Interface is the visible and interactive aspect of the running system. Windows, icons, menus, and guidelines (WIMP) are the middle elements of maximum modern-day graphical person interfaces (GUIs).
- The UI serves as the bridge between customers and the underlying machine, offering an intuitive means to navigate and engage with programs.
File System Management:
- Operating systems manipulate document systems, organizing statistics into files and directories. This consists of duties including creating, deleting, copying, and transferring files.
- File systems make sure efficient garage and retrieval of facts, with options like NTFS, FAT32, HFS, and ext4, relying on the OS.
Memory Management:
- Efficient reminiscence management is a critical characteristic of the OS, making sure that packages have get entry to to the vital sources.
- Tasks inclusive of digital memory allocation, swapping records between RAM and storage, and reminiscence protection mechanisms fall beneath the purview of the OS.
Process and Task Management:
- The OS oversees the execution of approaches, handling duties, and allocating system resources. This consists of multitasking, where a couple of programs run concurrently.
- Process scheduling algorithms prioritize tasks, optimizing device overall performance and responsiveness.
Device Drivers and Peripheral Interaction:
- Operating systems use device drivers to speak with hardware components. These drivers act as intermediaries, translating excessive-degree commands from the OS into instructions the hardware can understand.
- Plug and Play capability allows seamless integration of recent hardware devices without guide motive force set up in many contemporary operating systems.
Security Features:
- OS safety capabilities, including user account control, document permissions, and integrated firewalls, defend the gadget from unauthorized get entry to and malicious software program.
- Regular updates and patches supplied by OS builders assist in coping with protection vulnerabilities and ensure a strong defense against evolving threats.
Conclusion: The PC working device is the silent enabler, reworking a group of hardware additives into a powerful, person-friendly device. From the beauty of the personal interface to the complex orchestration of system sources, the OS performs a pivotal function in shaping our digital reports. As technology continues to advance, the evolution of PC working systems stays at the leading edge, adapting to new demanding situations and innovations even as steadfastly serving as the spine of modern-day computing.
Related Topics:




Well-balanced combination of text and visuals.
ReplyDeleteThe practical tips you share are a game-changer. Thanks for making a difference!"
ReplyDelete